
Kattenhorn SA, Hurford TA (2009) In: Pappalardo RT, McKinnon WB, Khurana K (eds) Tectonics of Europa. Kattenhorn SA (2004) Strike-slip fault evolution on Europa: evidence from tailcrack geometries. EOS Trans AGU (Spring Meet Suppl) 81, #S291 Jaeger WL, Turtle EP, McEwen AS, Keszthelyi LP, the Galileo SSI Team (2000) Possible tectonic origin for Hi’iaka Patera, Io. Hoppa G, Tufts BR, Greenberg R, Geissler P (1999) Strike–slip faults on Europa: global shear patterns driven by tidal stress. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 401 In: Platz T, Massironi M, Byrne PK, Hiesinger H (eds) Volcanism and tectonism across the inner solar system. Harris LB, Bédard JH (2014) Interactions between continent-like ‘drift’, rifting and 2034 mantle flow on Venus: gravity interpretations and Earth analogues. Icarus 206:210–228įorsythe LM, Zimbelman JR (1988) Is the Gordii Dorsum escarpment on Mars an exhumed transcurrent fault? Nature 336:143–146. Lunar Planet Sci Conf XXXIV, abstract #2033, Houstonįernández C, Anguita F, Ruiz J, Romeo I, Martín-Herrero ÀI, Rodrígue A, Pimentel C (2010) Structural evolution of Lavinia Planitia, Venus: implications for the tectonics of the lowland plains. Geological Society, LondonĭeRemer LC, Pappalardo RT (2003) Manifestations of strike-slip faulting on Ganymede. In: Cunningham WD, Mann P (eds) Tectonics of strike-slip restraining and releasing bends, Geological Society, special publications 290. Planet Space Sci 58:1286–1297Ĭunningham WD, Mann P (2007) Tectonics of strike-slip restraining and releasing bends. Icarus 207:868–886Ĭhetty TRK, Venkatrayudu M, Venkatasivappa V (2010) Structural architecture and a new tectonic perspective of Ovda Regio, Venus. Icarus 117:219–249īunte MK, Williams DA, Greeley R, Jaeger WL (2010) Geologic mapping of the Hi’iaka and Shamshu regions of Io. īrown CD, Grimm RE (1995) Tectonics of Artemis Chasma: a Venusian “plate” boundary. Planet Space Sci 52:215–222īorraccini F, Di Achille G, Ori GG, Wezel FC (2007) Tectonic evolution of the eastern margin of the Thaumasia Plateau (Mars) as inferred from detailed structural mapping and analysis. 36th Lunar Planet Sci Conf, abstract #2225, Houstonīistacchi N, Massironi M, Baggio P (2004) Large-scale fault kinematic analysis in Noctis Labyrinthus (Mars). Icarus 185(2):331–357Īrtita KS, Schultz RA (2005) Significance of deformation band-like strike slip faults on Mars.
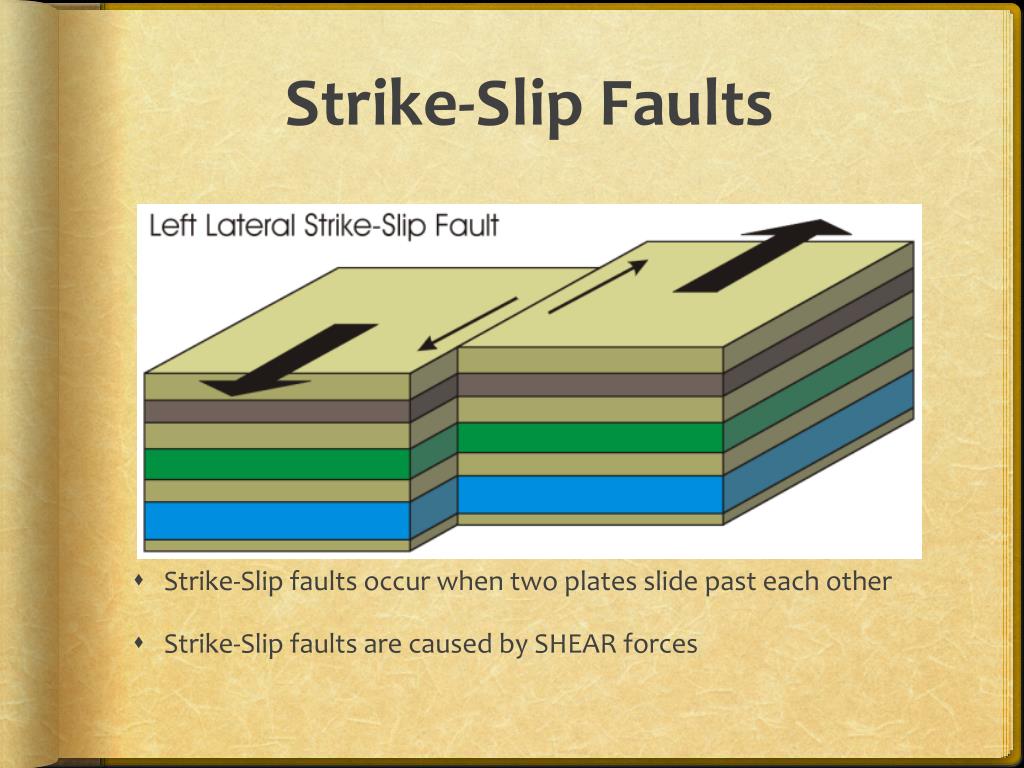
doi:10.1029/2007JE002980Īnguita F, Fernández C, Cordero G, Carrasquilla S, Anguita J et al (2006) Evidences for a Noachian–Hesperian orogeny in Mars. Video showing motion in a strike-slip fault.īends along strike-slip faults create areas of compression or tension between the sliding blocks (see Chapter 2).Andrews-Hanna JC, Zuber MT, Hauck SA II (2008) Strike-slip faults on Mars: observations and implications for global tectonics and geodynamics. If the opposing block moves right, it is dextral motion. If the block on the opposing side of the fault moves left relative to the observer’s block, this is called sinistral motion. The direction of the strike-slip movement is determined by an observer standing on a block on one side of the fault. In pure strike-slip motion, fault blocks on either side of the fault do not move up or down relative to each other, rather move laterally, side to side. Strike-slip faults are most commonly associated with transform plate boundaries and are prevalent in transform fracture zones along mid-ocean ridges. Strike-slip faults have side-to-side motion. \): Ketobe Knob in the San Rafael Swell of Utah displays an example of a thrust fault.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
